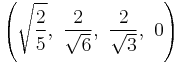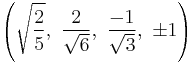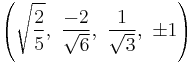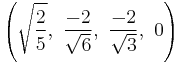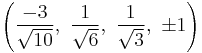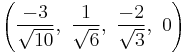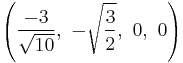Rectified 5-cell
| Rectified 5-cell | ||
Schlegel diagram with the 5 tetrahedral cells shown. |
||
| Type | Uniform polychoron | |
| Schläfli symbol | t1{3,3,3} | |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram | ||
| Cells | 10 | 5 {3,3} 5 3.3.3.3 |
| Faces | 30 {3} | |
| Edges | 30 | |
| Vertices | 10 | |
| Vertex figure | Triangular prism |
|
| Symmetry group | A4, [3,3,3], order 120 | |
| Petrie Polygon | Pentagon | |
| Properties | convex, isogonal, isotoxal | |
| Uniform index | 1 2 3 | |
In four dimensional geometry, the rectified 5-cell is a uniform polychoron composed of 5 regular tetrahedral and 5 regular octahedral cells. Each edge has one tetrahedron and two octahedra. Each vertex has two tetrahedra and three octahedra. In total it has 30 triangle faces, 30 edges, and 10 vertices. Each vertex is surrounded by 3 octahedra and 2 tetrahedra; the vertex figure is a triangular prism.
It is one of three semiregular polychora made of two or more cells which are platonic solids, discovered by Thorold Gosset in his 1900 paper. He called it a Tetroctahedric for being made of tetrahedron and octahedron cells.
The vertex figure of the rectified 5-cell is a uniform triangular prism, formed by three octahedra around the sides, and two tetrahedra on the opposite ends.
Contents |
Alternate names
- Dispentachoron
- Rectified 5-cell (Norman W. Johnson)
- Rectified 4-simplex
- Rectified pentachoron (Acronym: rap) (Jonathan Bowers)
- Ambopentachoron (Neil Sloane & John Horton Conway)
Images
| Ak Coxeter plane |
A4 | A3 | A2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graph | |||
| Dihedral symmetry | [5] | [4] | [3] |
stereographic projection (centered on octahedron) |
Net (polytope) |
| Tetrahedron-centered perspective projection into 3D space, with nearest tetrahedron to the 4D viewpoint rendered in red, and the 4 surrounding octahedra in green. Cells lying on the far side of the polytope have been culled for clarity (although they can be discerned from the edge outlines). The rotation is only of the 3D projection image, in order to show its structure, not a rotation in 4D space. |
Coordinates
The Cartesian coordinates of the vertices of an origin-centered rectified 5-cell having edge length 2 are:
|
|
|
More simply, the vertices of the rectified 5-cell can be positioned on a hyperplane in 5-space as permutations of (0,0,0,1,1) or (0,0,1,1,1). These construction can be seen as positive orthant facets of the rectified pentacross or birectified penteract respectively.
Related polychora
This polytope is the vertex figure of the 5-demicube, and the edge figure of the uniform 221 polytope.
It is also one of 9 uniform polychora constructed from the [3,3,3] Coxeter group.
| Name | 5-cell | truncated 5-cell | rectified 5-cell | cantellated 5-cell | bitruncated 5-cell | cantitruncated 5-cell | runcinated 5-cell | runcitruncated 5-cell | omnitruncated 5-cell |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Schläfli symbol |
{3,3,3} | t0,1{3,3,3} | t1{3,3,3} | t0,2{3,3,3} | t1,2{3,3,3} | t0,1,2{3,3,3} | t0,3{3,3,3} | t0,1,3{3,3,3} | t0,1,2,3{3,3,3} |
| Coxeter-Dynkin diagram |
|||||||||
| Schlegel diagram |
|||||||||
| A4 Coxeter plane Graph |
|||||||||
| A3 Coxeter plane Graph |
|||||||||
| A2 Coxeter plane Graph |
See also
References
- T. Gosset: On the Regular and Semi-Regular Figures in Space of n Dimensions, Messenger of Mathematics, Macmillan, 1900
- H.S.M. Coxeter:
- H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edition, Dover New York, 1973
- Kaleidoscopes: Selected Writings of H.S.M. Coxeter, editied by F. Arthur Sherk, Peter McMullen, Anthony C. Thompson, Asia Ivic Weiss, Wiley-Interscience Publication, 1995, ISBN 978-0-471-01003-6 [1]
- (Paper 22) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi Regular Polytopes I, [Math. Zeit. 46 (1940) 380-407, MR 2,10]
- (Paper 23) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes II, [Math. Zeit. 188 (1985) 559-591]
- (Paper 24) H.S.M. Coxeter, Regular and Semi-Regular Polytopes III, [Math. Zeit. 200 (1988) 3-45]
- Norman Johnson Uniform Polytopes, Manuscript (1991)
- N.W. Johnson: The Theory of Uniform Polytopes and Honeycombs, Ph.D. (1966)
External links
- Rectified 5-cell - data and images
- Richard Klitzing, 4D uniform polytopes (polychora), x3o3o3o - rap